E-commerce in Japan: Exploring the opportunities and challenges of selling products or services online in the Japanese market
Entering the Japanese E-commerce Market: Unveiling Opportunities and Challenges
The Japanese e-commerce market is a thriving landscape that offers immense opportunities for foreign companies. With its impressive size and steady growth rate, it has become a focal point for businesses seeking expansion. In this blog post, we will delve into the details of the Japanese e-commerce market, analyze consumer behavior, explore successful case studies, highlight failures, and outline key success factors for foreign brands. Additionally, we will emphasize the importance of consulting with local market entry experts such as DGC for a seamless entry into this dynamic market.
The Japanese e-commerce market is an economic powerhouse, with an estimated size of $200 billion in 2022 according to Global Data.
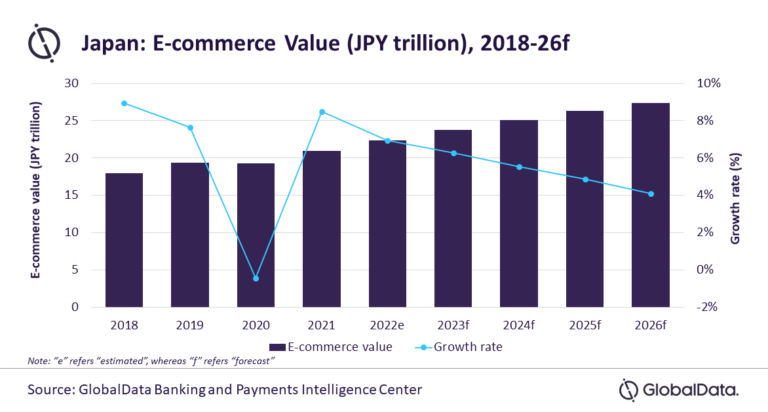
It boasts a remarkable growth rate of 9% year-over-year, driven by various industries including electronics, fashion, beauty, and more. For example, the electronics segment accounts for approximately 35% of the overall e-commerce market, while fashion and beauty have experienced significant growth, contributing 20% and 15%, respectively. These trends present exciting opportunities for foreign companies aiming to enter the market.
Opportunities and challenges in Japanese E-commerce market for foreign companies:
Let’s delve into the details of the opportunities and challenges in the Japanese e-commerce market:
Opportunities
- Increasing internet penetration and smartphone usage: Japan has a high rate of internet penetration and widespread smartphone adoption. This means that a large portion of the population has access to online platforms, creating a vast market for e-commerce businesses to tap into.
- A large consumer base with high purchasing power: Japan has a significant population of tech-savvy consumers with relatively high disposable incomes. This provides a strong consumer base that is willing to engage in online shopping and has the purchasing power to support e-commerce businesses.
- Growing demand for foreign products and services: Japanese consumers are increasingly interested in foreign products and services, including fashion, cosmetics, electronics, and more. This presents an opportunity for foreign brands to leverage their unique offerings and cater to this demand through e-commerce channels.
- Favorable government policies supporting e-commerce growth: The Japanese government has implemented policies and initiatives to support the growth of the e-commerce sector. This includes measures to streamline logistics and customs processes, promote cross-border trade, and facilitate online transactions, making it easier for foreign companies to enter the market.
Challenges
- Intense competition from domestic and international players
The Japanese e-commerce market is highly competitive, with both domestic and international players vying for consumer attention. This requires foreign companies to differentiate themselves through unique value propositions, localized strategies, and superior customer experiences. - Language and cultural barriers
Japanese is the primary language spoken in Japan, and while there is a growing number of English-speaking consumers, a significant portion of the population prefers to conduct transactions in Japanese. Overcoming language and cultural barriers by providing localized content, customer support, and user experiences is essential for foreign brands to succeed. - Complex regulatory landscape
Japan has specific regulations and compliance requirements related to e-commerce, consumer protection, data privacy, and more. Navigating this complex regulatory landscape can be challenging for foreign companies, requiring them to ensure legal compliance and understand the intricacies of the local business environment. - Building trust and establishing credibility among Japanese consumers
Japanese consumers place a strong emphasis on trust and credibility when making online purchases. Foreign brands may face initial skepticism, as consumers tend to prioritize established domestic brands. Gaining the trust of Japanese consumers requires consistent delivery of high-quality products, excellent customer service, and building brand reputation through positive customer reviews and recommendations.
Understanding these challenges and opportunities is crucial for foreign brands looking to enter the Japanese e-commerce market. By addressing language and cultural barriers, navigating the regulatory landscape, differentiating from competitors, and building trust with consumers, businesses can increase their chances of success in this dynamic market.
Japanese Consumer Behavior in E-commerce
Japanese consumers are tech-savvy and enthusiastic adopters of e-commerce. They actively seek out foreign products and services, contributing to the popularity of cross-border online shopping. Key factors influencing their buying decisions include:
- Quality and authenticity of products
Japanese consumers value high-quality products and place great importance on authenticity. They seek out trusted brands known for delivering reliable and genuine products. Foreign brands entering the Japanese e-commerce market should prioritize product quality and ensure transparent information about the origin, manufacturing processes, and certifications of their offerings. - Trusted brand reputation
Building trust is crucial for success in the Japanese e-commerce market. Japanese consumers often rely on brand reputation and customer reviews to make purchasing decisions. Foreign brands should focus on establishing credibility by showcasing positive customer feedback, highlighting partnerships with reputable companies, and leveraging influencer marketing strategies to gain trust. - Competitive pricing
Japanese consumers are savvy shoppers who compare prices across different platforms before making a purchase. They appreciate competitive pricing and often look for deals and discounts. Foreign brands need to carefully consider their pricing strategies to align with market expectations and offer value to Japanese consumers. - Reliable customer service
Excellent customer service is highly valued by Japanese consumers. They expect prompt and courteous assistance before, during, and after the purchase process. Offering responsive customer support channels, addressing queries and concerns promptly, and providing clear communication in Japanese language can greatly enhance the customer experience. - Secure payment options
Japanese consumers prioritize secure and convenient payment options. Local payment methods like credit cards, convenience store payments, and digital wallets (such as Rakuten Pay and LINE Pay) are popular in Japan. Foreign brands should ensure a seamless and secure payment process to instill confidence in consumers. - Fast and efficient delivery
Japanese consumers have high expectations when it comes to delivery speed and reliability. They value fast shipping and prefer options with short delivery times. Providing efficient logistics and partnering with reliable shipping providers to ensure timely deliveries can significantly impact customer satisfaction and repeat purchases.
By understanding these factors and incorporating them into their e-commerce strategies, foreign brands can better cater to the preferences and needs of Japanese consumers. Prioritizing product quality, building trust through brand reputation, offering competitive pricing, delivering exceptional customer service, providing secure payment options, and ensuring fast and efficient delivery are key steps toward success in the Japanese e-commerce market.
Amazon
An example of a foreign brand that has achieved success in the Japanese e-commerce market is Amazon. With its global reach and extensive product offerings, Amazon was able to tap into the Japanese market and establish a strong presence. By localizing its website and tailoring its services to cater to Japanese consumers, Amazon effectively addressed language and cultural barriers. Moreover, the company prioritized fast and reliable delivery services, providing a seamless customer experience. Amazon’s success can be attributed to its ability to adapt to local market dynamics and meet the preferences and expectations of Japanese consumers.
ASOS
Here’s another example of a foreign brand that achieved success in the Japanese e-commerce market:
ASOS, the UK-based online fashion and beauty retailer, experienced notable success in the Japanese market. Here are some reasons behind their achievement:
- Extensive product range
ASOS offers a vast selection of fashion items, including clothing, accessories, and beauty products. Their extensive range caters to diverse style preferences and allows Japanese consumers to find unique and trendy items that align with their individual tastes. - International brand appeal:
ASOS leveraged its international brand appeal and positioned itself as a go-to destination for global fashion trends. Japanese consumers, particularly younger demographics, were drawn to ASOS for its range of international brands and access to styles popular in Western markets. - Size inclusivity
ASOS has made strides in offering a wide range of sizes to cater to diverse body types. This inclusive approach resonated well with Japanese consumers who appreciate options that fit their individual shapes and sizes. - Influencer collaborations
ASOS collaborated with influential Japanese fashion influencers and celebrities to create exclusive collections and promote their brand. These partnerships helped ASOS gain visibility and credibility within the local market, attracting a wider customer base. - Seamless mobile shopping experience:
ASOS prioritized mobile optimization, providing a user-friendly and seamless shopping experience through their mobile app. With a significant portion of Japanese consumers using smartphones for online shopping, ASOS’s mobile-focused strategy allowed them to reach and engage with their target audience effectively. - Social media engagement
ASOS actively engaged with their Japanese customers through social media platforms like Instagram and Twitter. They shared fashion inspiration, style tips, and user-generated content, fostering a sense of community and strengthening their brand presence in the Japanese market.
By offering an extensive product range, leveraging international brand appeal, embracing size inclusivity, collaborating with influencers, providing a seamless mobile shopping experience, and engaging with customers through social media, ASOS successfully captured the attention and loyalty of Japanese consumers in the e-commerce space.
Apple
Apple is indeed another example of a foreign brand that has achieved remarkable success in the Japanese e-commerce market. Here are some reasons behind Apple’s success:
- Strong brand reputation
Apple has built a strong brand reputation globally, including in Japan. The brand’s focus on quality, innovation, and user experience has resonated well with Japanese consumers who appreciate reliable and technologically advanced products. - High demand for Apple products
Japanese consumers have shown a significant interest in Apple products, including iPhones, iPads, MacBooks, and Apple Watches. The sleek design, cutting-edge technology, and seamless integration between Apple devices have contributed to the brand’s popularity in the Japanese market. - User-friendly online store
Apple’s online store provides a user-friendly and intuitive shopping experience. Japanese consumers can easily browse and purchase Apple products directly from the official website, with detailed product information, customization options, and transparent pricing. - Localized marketing and support
Apple has implemented localized marketing strategies to cater to Japanese consumers. This includes Japanese language support across their website, advertisements featuring local celebrities, and campaigns tailored to Japanese cultural preferences and seasonal events. Apple also offers customer support in Japanese, ensuring a positive experience for users. - Strong retail presence
In addition to the online store, Apple has established a strong retail presence in Japan with various Apple Stores and authorized resellers. This omnichannel approach allows customers to experience Apple products firsthand and receive in-person assistance, creating a seamless shopping experience. - Apple ecosystem and services
Apple’s ecosystem, which includes iCloud, Apple Music, and the App Store, enhances the overall customer experience and adds value to their products. Japanese consumers appreciate the convenience and integration of these services, further contributing to Apple’s success in the e-commerce market.
By leveraging its strong brand reputation, meeting the high demand for its products, providing a user-friendly online store, implementing localized marketing and support, establishing a robust retail presence, and offering a comprehensive ecosystem of services, Apple has achieved remarkable success in the Japanese e-commerce market.
Target Corporation
One example of a foreign brand that faced challenges and failed to establish a successful presence in the Japanese e-commerce market is Target Corporation.
Target, a well-known retail brand in the United States, entered the Japanese market with high hopes but encountered significant difficulties. The company struggled to understand the unique preferences and shopping habits of Japanese consumers. They faced challenges related to localization, product assortment, and pricing strategies. Additionally, Target faced tough competition from established domestic retailers and failed to differentiate itself effectively.
More details about Target’s challenges and failure in establishing a successful presence in the Japanese e-commerce market:
- Localization difficulties
Target faced challenges in understanding and adapting to the unique preferences and shopping habits of Japanese consumers. The company struggled to effectively localize its brand and offerings to cater to the local market. This included issues with language barriers, cultural differences, and differing consumer expectations compared to the American market. - Product assortment mismatch
Target initially brought a similar product assortment to Japan as in their home market, which didn’t resonate well with Japanese consumers. The brand failed to accurately gauge the demand for certain product categories and did not offer a compelling selection that aligned with local consumer preferences. The lack of localized and tailored product offerings hindered their ability to capture the attention and loyalty of Japanese consumers. - Pricing challenges
Target also faced difficulties with pricing strategies in the Japanese market. The company struggled to find the right balance between competitive pricing and profitability, as they faced pressure from both established domestic retailers and other international brands. This posed challenges in positioning themselves effectively in terms of price perception and value proposition. - Intense competition
Japan has a highly competitive retail market, with strong domestic retailers that have established a deep understanding of local consumer preferences. Target faced tough competition from well-established Japanese retailers who had already built strong relationships with consumers. This made it challenging for Target to differentiate itself and gain a significant market share. - Failure to differentiate
Despite efforts to adapt and localize, Target failed to differentiate itself effectively from the competition. They were unable to clearly communicate their unique value proposition and failed to offer compelling reasons for Japanese consumers to choose Target over other established retailers. This lack of differentiation contributed to their struggles in gaining traction and building a loyal customer base.
As a result of these challenges and the inability to overcome them, Target made the difficult decision to withdraw from the Japanese market in 2002 after six years of operation. This example highlights the importance of thoroughly understanding local consumer behavior, preferences, and competition when entering a new market. It underscores the need for foreign brands to invest in comprehensive market research, localization efforts, and a tailored approach to succeed in the Japanese e-commerce market.
Another example of a foreign brand that faced challenges and failed to establish a successful presence in the Japanese e-commerce market is Tesco, a British multinational grocery and general merchandise retailer.
Tesco
Tesco entered the Japanese market in 2003 with the acquisition of a local supermarket chain called C Two-Network. However, despite its success in the UK and other international markets, Tesco encountered significant difficulties in Japan and eventually decided to exit the market in 2011. Here are some key challenges faced by Tesco:
- Cultural differences and consumer preferences
Tesco struggled to understand and adapt to the unique cultural preferences of Japanese consumers. Japanese customers have distinct shopping habits and a strong preference for fresh and local produce. Tesco’s focus on efficiency and low prices, which worked well in other markets, did not align with the expectations and preferences of Japanese shoppers. - Intense competition
The Japanese grocery market is highly competitive, with strong domestic players that have a deep understanding of local consumer needs and preferences. Tesco faced fierce competition from well-established supermarket chains and struggled to differentiate itself effectively. The company was unable to gain a significant market share and failed to attract a loyal customer base. - Supply chain challenges
Tesco faced difficulties in managing its supply chain efficiently in Japan. The company struggled with maintaining a reliable and consistent supply of fresh produce, which is highly valued by Japanese consumers. This affected the quality and availability of products in Tesco stores, further hindering their ability to attract and retain customers. - Expansion limitations
Tesco’s expansion strategy in Japan involved acquiring existing supermarket chains. However, this approach limited their flexibility and ability to fully integrate their operations and implement their own successful retail model. The challenges of integrating the acquired stores and aligning them with Tesco’s brand image and customer experience standards posed additional hurdles. - Economic downturn and timing
Tesco’s entry into the Japanese market coincided with a period of economic downturn in Japan. The timing was unfavorable, as consumers were cutting back on spending, and competition among retailers intensified. This challenging economic climate further exacerbated the difficulties faced by Tesco in establishing a successful presence.
These challenges, combined with the failure to understand and adapt to local consumer preferences, led to Tesco’s decision to exit the Japanese market. The example of Tesco highlights the importance of thorough market research, understanding cultural nuances, and tailoring strategies to local consumer preferences when entering the Japanese e-commerce market.
Key Success Factors and Solutions for Foreign Brands To ensure success in the Japanese e-commerce market, foreign brands must consider the following key factors:
- Conduct comprehensive market research and understand consumer behavior:
Thorough market research is essential to understand the unique preferences, needs, and buying behavior of Japanese consumers. It involves analyzing market trends, competitive landscape, and consumer insights. This research will help foreign brands tailor their offerings, marketing strategies, and customer experience to effectively target the Japanese market. - Localize websites, content, and marketing strategies:
Localization is crucial for success in the Japanese market. It involves adapting websites, content, and marketing materials to resonate with Japanese consumers. This includes translating content into Japanese, ensuring culturally appropriate messaging, and incorporating local nuances and references. By speaking directly to the target audience in their language and addressing their specific needs, foreign brands can build trust and connection with Japanese consumers. - Build relationships with local influencers and form strategic partnerships:
Influencer marketing plays a significant role in the Japanese market. Partnering with local influencers who have a strong following and influence can help increase brand visibility and credibility. Additionally, forming strategic partnerships with local retailers or online platforms can provide access to a wider customer base and enhance brand recognition in Japan. - Provide exceptional customer service and support:
Japanese consumers place a high value on exceptional customer service. Foreign brands should prioritize providing responsive and reliable customer support to address any inquiries or issues promptly. Implementing local customer service channels, such as Japanese-language support and local contact numbers, can further enhance the customer experience and build trust with Japanese shoppers. - Optimize logistics and delivery processes:
Fast and reliable delivery is crucial for success in the Japanese e-commerce market. Foreign brands should optimize their logistics and supply chain operations to ensure timely delivery of products. Collaborating with reputable logistics partners in Japan and offering convenient delivery options, such as same-day or next-day delivery, can give foreign brands a competitive edge. - Leverage the expertise of local market entry consultants:
Collaborating with local market entry consultants, such as DGC, can provide invaluable insights and guidance tailored to the Japanese market. We have in-depth knowledge of the local business landscape, consumer behavior, and regulatory requirements. They can help foreign brands navigate challenges, identify growth opportunities, and develop effective market entry strategies.